Arm unveils next-gen Neoverse CPU cores and compute subsystems — hoping to entice more custom silicon customers
February 22, 2024
Micron shows massive 256GB DDR5-8800 memory sticks — High-capacity double-height 20-watt MCRDIMM modules come in different flavors
March 22, 2024Firmware update to disable the Current Excursion Protection in beta
which allows you to turn off the CEP (Current Excursion Protection) function. According to the vendor's findings, disabling CEP can make your Intel 14th Generation Raptor Lake Refresh non-K processor run cooler without compromising performance.
Some users run their processors at stock, while others overclock them. Others like to undervolt their processors to make them run cooler while also saving some energy. However, MSI discovered that undervolting Raptor Lake Refresh non-K chips harms performance. The main culprit is the CEP. CEP is a protection function that impedes instability when insufficient voltage goes to the processor. When you undervolt Raptor Lake Refresh non-K SKUs, this triggers CEP, imposing a performance penalty on the chip through throttling.
which allows you to turn off the CEP (Current Excursion Protection) function. According to the vendor's findings, disabling CEP can make your Intel 14th Generation Raptor Lake Refresh non-K processor run cooler without compromising performance.
Some users run their processors at stock, while others overclock them. Others like to undervolt their processors to make them run cooler while also saving some energy. However, MSI discovered that undervolting Raptor Lake Refresh non-K chips harms performance. The main culprit is the CEP. CEP is a protection function that impedes instability when insufficient voltage goes to the processor. When you undervolt Raptor Lake Refresh non-K SKUs, this triggers CEP, imposing a performance penalty on the chip through throttling.
| CPU / Chipset | Z790/Z690 MB | B760/B660 MB |
|---|---|---|
| 14th Gen K-series | Yes (already supported with previous microcode) | Yes |
| 14th Gen non-K series (BO stepping) | Yes | Yes |
| 14th Gen non-K series (other stepping) | No | No |
| 13th Gen K-series | Yes | No |
| 13th Gen non-K series | No | No |
| 12th Gen K-series | Yes | No |
| 12th Gen non-K series | No | No |
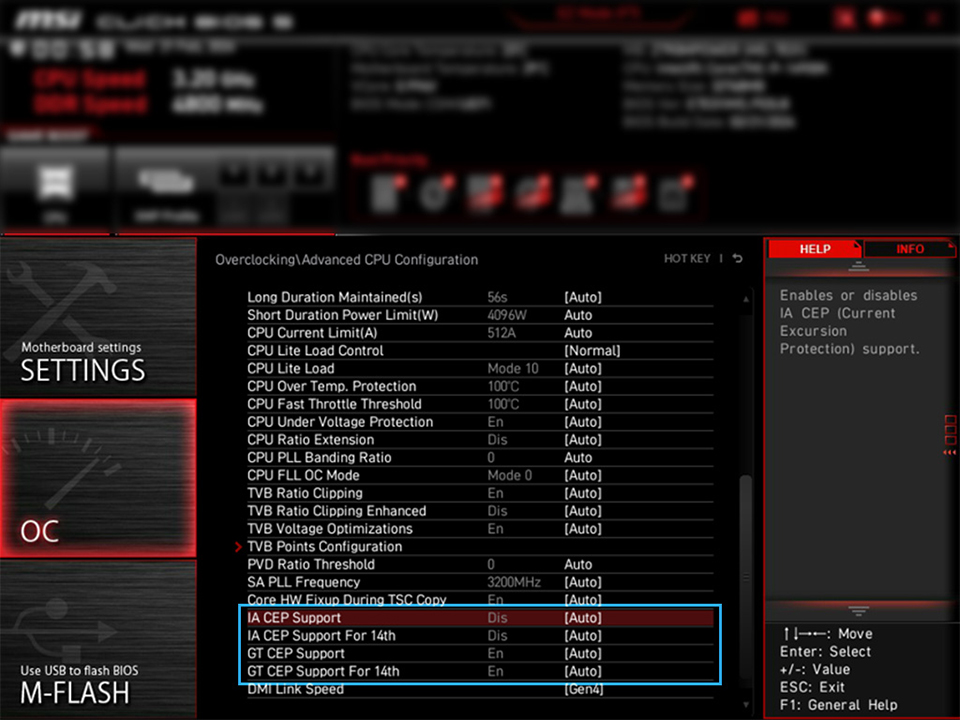
The CEP option is located inside the motherboard's BIOS. The exact location may vary depending on the motherboard model. However, the option typically resides in the Advanced CPU Configuration section under the Overclocking tab.
You might find two different CEP options: IA CEP and GT CEP. The former corresponds to the processor's cores, whereas the latter is for the chip's iGPU.
MSI is deploying the new firmware with the updated Intel microcode in two waves. The first wave consists of Z790 and B760 motherboards, while the second includes the B760 and 600-series motherboards. The first batch of firmware is already available for download at MSI's website, while the second batch is scheduled for a late March release.
One thing to note is that MSI's firmware is in the beta phase, so there are bound to be some bugs. If you don't own a non-K processor or don't plan on undervolting it, you can probably pass on this update.